Dry eye is a chronic ocular surface disease caused by multiple factors. It is caused by abnormalities in the quality, quantity, and dynamics of tears, leading to instability of the tear film or imbalance of the ocular microenvironment. It is often accompanied by ocular inflammatory reactions, tissue damage, and neurological abnormalities, resulting in various discomfort symptoms and/or visual function disorders in the eyes. The core mechanism of dry eye is the high osmotic pressure of tears, which is also one of the characteristics of dry eye. The high osmotic pressure of tears can directly or indirectly cause inflammation and damage to the ocular surface. The tear film is mainly composed of lipid layer, aqueous layer, and mucin layer. Through tear dynamics (including blinking, etc.), tears are distributed on the ocular surface and finally expelled from the eye. Therefore, maintaining the stability of the tear film, preventing excessive evaporation of tears, and maintaining the fluidity of the ocular surface fluid are fundamental measures for dry eye treatment.
EYESIS Constant Fumigation Treatment Device DEA Series Products Launched

Function Parameter
Scope of application: This product is used for the treatment of dry eye patients mainly with meibomian gland dysfunction.Dry eye is a chronic ocular surface disease caused by multiple factors. It is caused by abnormalities in the quality, quantity, and dynamics of tears, leading to instability of the tear film or imbalance of the ocular microenvironment. It is often accompanied by ocular inflammatory reactions, tissue damage, and neurological abnormalities, resulting in various discomfort symptoms and/or visual function disorders in the eyes. The core mechanism of dry eye is the high osmotic pressure of tears, which is also one of the characteristics of dry eye. The high osmotic pressure of tears can directly or indirectly cause inflammation and damage to the ocular surface. The tear film is mainly composed of lipid layer, aqueous layer, and mucin layer. Through tear dynamics (including blinking, etc.), tears are distributed on the ocular surface and finally expelled from the eye. Therefore, maintaining the stability of the tear film, preventing excessive evaporation of tears, and maintaining the fluidity of the ocular surface fluid are fundamental measures for dry eye treatment.
The constant temperature fumigation therapy device has the following functions: constant temperature hot fumigation, constant temperature cold fumigation, and drug introduction.
Mechanism

Mechanism of hot compress therapy::
The function of dilating blood vessels, improving local blood circulation, promoting local metabolism, and facilitating the absorption of inflammation. Hot compress restores the fluidity of the increased viscosity of the eyelid ester, facilitating its excretion and improving or restoring the function of the meibomian gland. The conventional hot compress method uses local heating to restore the fluidity of the increased viscosity of the eyelid ester, which is beneficial for the discharge to improve or restore the function of the meibomian gland and treat meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD).
Mechanism of cold compress therapy::
Activation of cold receptors, constriction of blood vessels, reduction of inflammatory substance release, alleviation of swelling, reduction of skin temperature increase caused by inflammatory substance release, and alleviation of discomfort; Reduce sensory nerve conduction velocity, increase pain threshold, and alleviate pain. There are receptors on the ocular surface that can sense cold stimuli, and dry eye patients may experience ocular surface damage and reduced corneal sensitivity, leading to a decrease in basal tear secretion and blink frequency. Cold compress can achieve local cooling, increase basal tear secretion, and thus improve dry eye symptoms.
Mechanism of drug delivery::
Regular fumigation with professional eye fumigation equipment in traditional Chinese medicine hospitals can better promote the flow and excretion of meibomian gland esters. Under the guidance of traditional Chinese medicine physicians, hospitals with conditions can use special Chinese medicines such as wild chrysanthemums, mulberry leaves, honeysuckle, and honeysuckle for fumigation, which can more quickly solve the clinical symptoms and signs of dry eye patients.
Clinical efficacy
Hot compress effectively maintains a constant temperature of 42.5 ℃, providing stable and moisturizing coverage of the eye surface. The combination of meibomian gland unblocking therapy and local constant temperature oxygen ultrasonic nebulization therapy has significant therapeutic effects on MGD related dry eye syndrome, which is beneficial for relieving dry eye symptoms, improving eye comfort, promoting tear film recovery, and enhancing patients' quality of life.
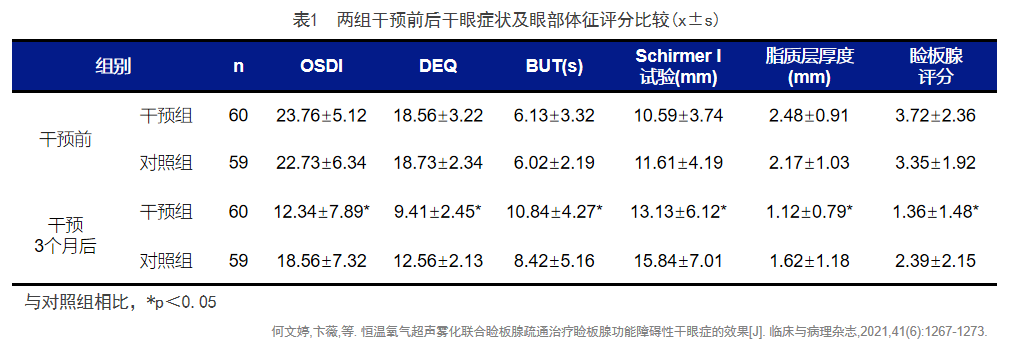
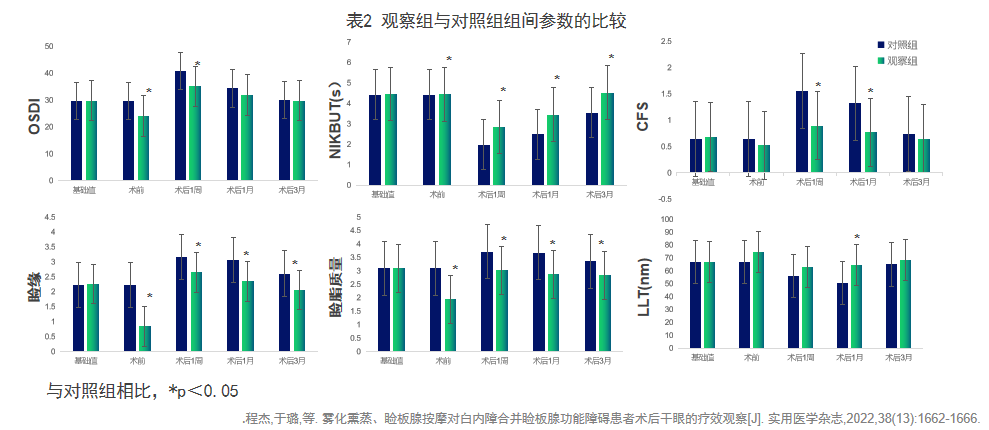
Nebulization fumigation combined with meibomian gland massage is effective for dry eye patients during cataract surgery. After comparing various parameters between the two groups, the observation group showed significantly higher NIKBUT, meibomian margin, and meibomian gland secretion quality scores during the cataract perioperative period compared to the control group. The postoperative meibomian congestion and meibomian gland opening obstruction in the observation group were significantly improved compared to the control group during the same period. Therefore, preoperative nebulization fumigation of MGD combined with meibomian gland massage therapy is effective in reducing dry eye caused by cataract surgery.
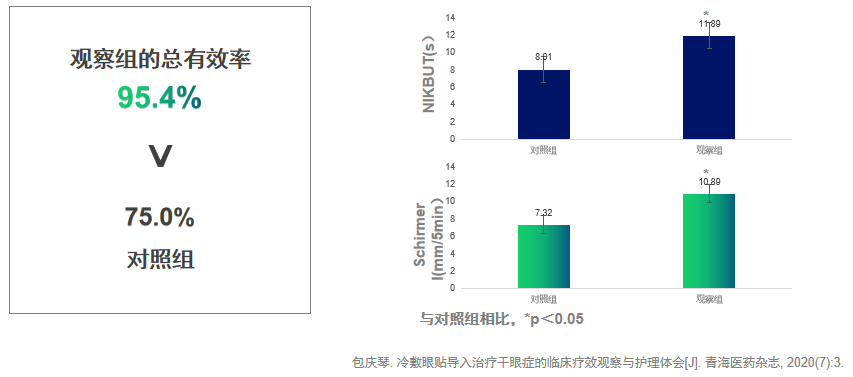
Ultra low cooling temperature, relieving inflammation and providing continuous comfort. Medical cold compress eye patch introduction therapy can further improve the clinical symptoms of dry eye syndrome, with significant effects. After treatment, the tear film rupture time (NIKBUT) and tear secretion volume (Schirmer I) of the two groups of patients were significantly increased compared to the observation group (11.89 ± 1.56) s and the control group (8.01 ± 1.42) s. The Schirmer I of the observation group (10.89 ± 1.06) mm/5 min was significantly decreased compared to the control group (7.32 ± 1.02) mm/5 min, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).